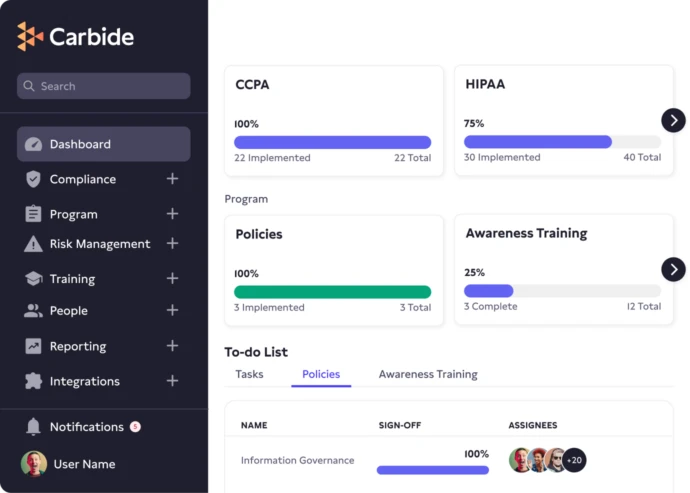
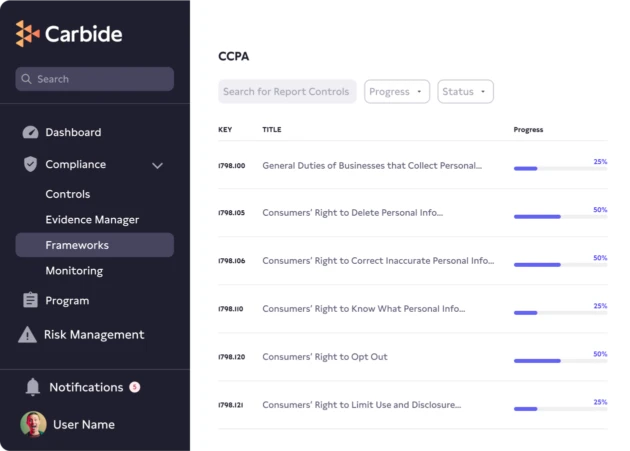
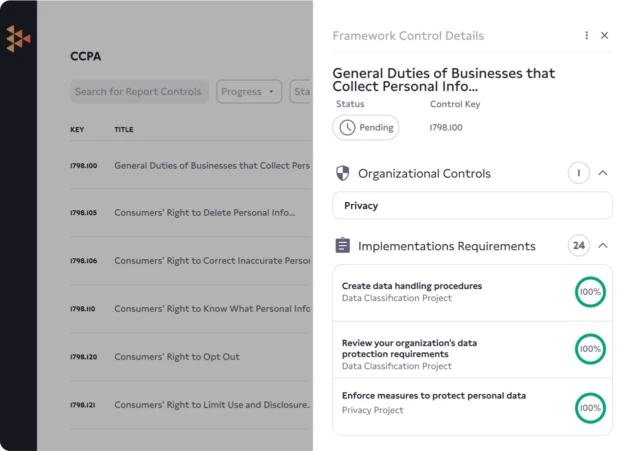
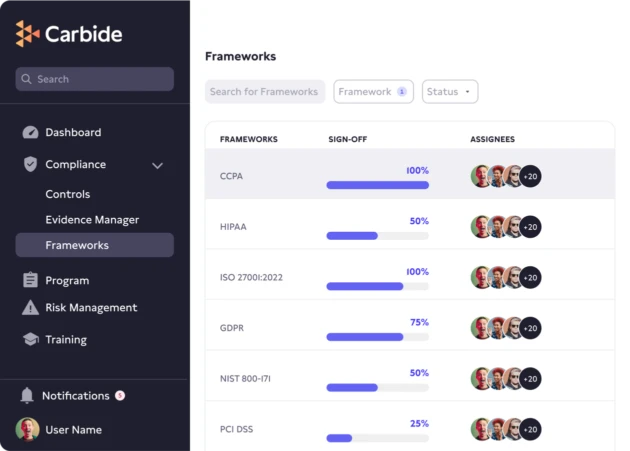
The California Consumer Privacy Act was established to give Californians privacy and data protection similar to the EU’s GDPR, but if you’re doing business in California, you have a legal obligation to comply with this regulation governing how for-profit businesses collect, use, and disclose personal information of California’s residents.
The Carbide Platform and its embedded DRIVE (Design, Review, Implement, Validate, & Evolve) approach to CCPA compliance gives you a step-by-step plan to ensure your business follows all 6 of CCPA’s Articles.