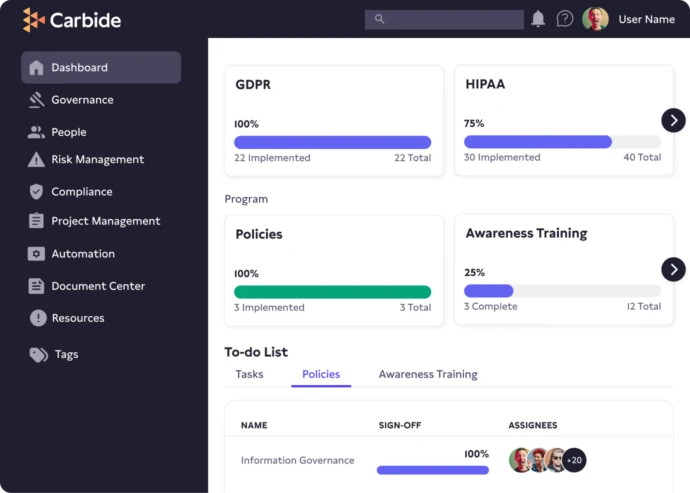
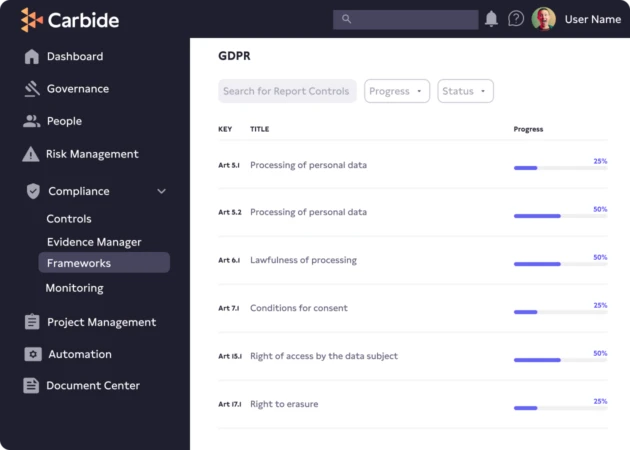
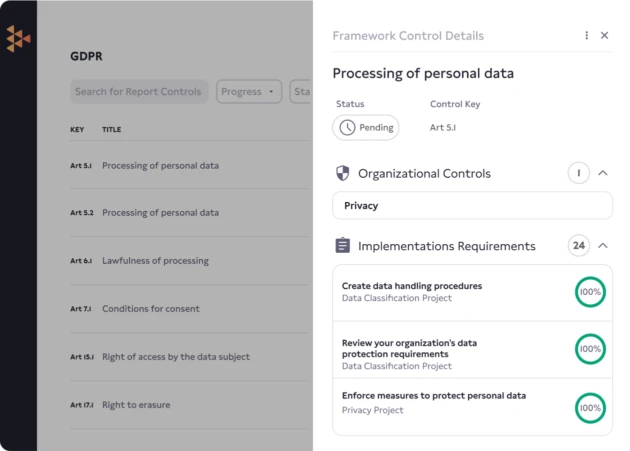
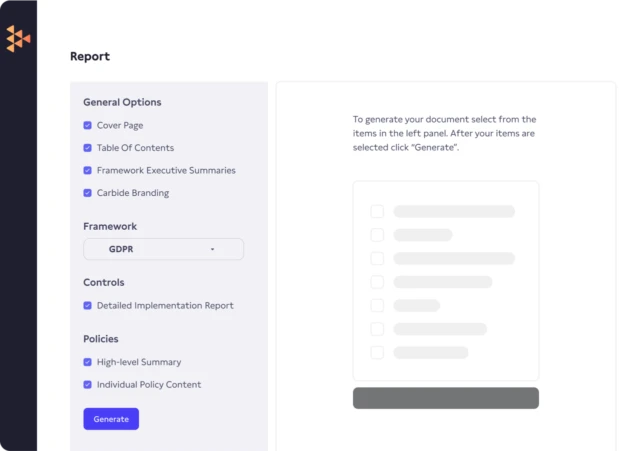
Assure customers you’re protecting their data. Getting compliant with the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a journey with many steps that have to conform to the European Union’s strict set of regulations for data protection. With Carbide, you’ll get a map, the best route, and a backpack full of essentials to ensure you reach your destination.
GDPR Compliance Software with Expert Support
Get your business compliant with Europe’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requirements
INTENTIONAL DATA PROTECTION LEADS TO FASTER COMPLIANCE
DRIVE security & privacy by design
Achieve compliance by default
Everything you need for GDPR compliance
-
GDPR Plan
Step by step implementation plan outlines every GDPR regulation and requirement
-
Customized Policies
Our automated policy builder ensures your policies meet GDPR requirements
-
Policy Management
Reduce admin time with automated employee reminders and tracking
-
Security Awareness Training
In-platform Carbide Academy videos on security and privacy best practices with a template library for common requirements
-
Evidence Collection
100+ technical integrations connecting to your tech stack to automatically capture your compliance with GDPR
-
Audit Support
Save time by giving auditors a read-only view of your GDPR reporting dashboard
-
Robust Ecosystem
Carbide’s security and privacy services and network of audit partners help you meet requirements faster
-
Multi-Compliance by Design
Comply with multiple frameworks & regulations with our unified platform
-
Cloud Monitoring
Easily collect data with automated security monitoring, security assessments, and remediation tools to make actionable insights on your cloud environment
Frequently Asked Questions
GDPR stands for the General Data Protection Regulation. It protects the citizens of the European Union and went into effect in May of 2018. The GDPR ensures that companies are held accountable for keeping personal information safe. Although this law was created in the European Union to protect the data of its citizens it affects companies that deal with worldwide business and handle data around the world. The GDPR set new standards for global privacy and initiated a wave of similar laws globally.
This principle within the GDPR institutes Privacy by Design as a primary element of data protection in which technologies are designed to include privacy as a default function rather than an option. In this way, when a user accesses a website or service, the default is that a data subject’s utmost privacy remains intact throughout the lifecycle of the data processing venture.
The data processor under the GDPR simply is the processor of the data that the Data Controller provides them. The data processor is a third party the controller chose to work with and to process the data, and they do not own the data and they do not control the data.
The GDPR regulates what companies can do with the data they collect and process about European citizens. These regulations apply to any business (including those based in the US and Canada) that stores or processes the data of European citizens. The most important feature of this privacy law is that it gives users more rights and control over what your business does with their data and whether they wish to consent to the collection of their data by your business.
Under GDPR, “pseudonymization” is a process required for all stored data. Pseudonymisation is the process that transforms how data is stored in a way that will make the final data not attributable to a specific data subject (person or company) without using any additional information. Pseudonymisation is an alternative to complete data anonymization. An example of pseudonymization is encryption.
As the title suggests, the Data Controller is in charge of data and they have the most responsibility in regards to the protection of privacy and the rights of “Data Subjects”. The controller is also the collector of data.
Under GDPR, the controller must disclose any and all data collection, disclose the lawful basis for and the purpose for data processing. They are also required to state the timeframe for data processing. They are also responsible to state the timeframe for data retention. Another requirement for controllers is that they must disclose if the data collected is being shared with any third parties or outside of the EEA.
See How Carbide Can Help You
Schedule a consultation with one of our Data Protection Solutions Advisors to learn how Carbide can accelerate your security & privacy program.