NIST and CIS are two organizations that publish some of the most comprehensive standards that modern businesses can adopt to improve their cybersecurity readiness. If you run an organization that handles sensitive information, cybersecurity standards most likely aren’t be new to you. Still, plenty of organizations offer “competing” standards, and if you’re in charge of making cybersecurity decisions, it can be hard to figure out which guidelines to follow.
NIST and CIS provide invaluable guidance for cybersecurity standards, but implementing and managing these standards effectively can be a complex and time-consuming task.
The Carbide Platform provides a centralized hub for managing your organization’s security posture, ensuring compliance with industry security frameworks like SOC 2, ISO 27001, NIST 800 171, NIST 800-53, and more. Take a self-guided tour of our platform to learn more.
In this article, we’ll introduce you to both organizations and discuss their differences and similarities.
What is NIST?
NIST stands for the National Institute of Standards and Technology. It’s a non-regulatory organization to advance technological adoption and increase standards for American companies. With the advent of networks and cybersecurity threats, NIST has taken on a more significant role in outlining standards and best practices for organizations to follow.
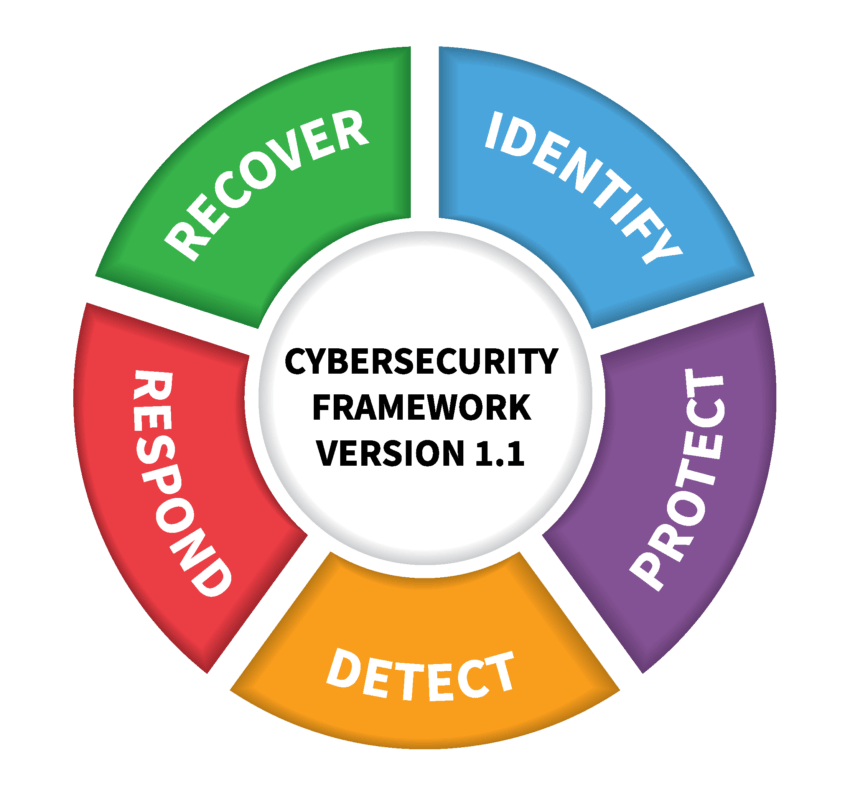
If you run a business that deals with sensitive information or Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), you’re probably aware of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF) and some specific publications, such as NIST 800-171.
The NIST CSF offers a comprehensive set of non-mandatory guidelines for organizations seeking to improve their cybersecurity practices. NIST 800-171 is one of over two hundred specific NIST publications, and that particular entry focuses on cybersecurity standards for Department of Defense contractors.
An Introduction to CIS
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) has been around since 2000. This organization’s goal is to help public and private businesses to adopt better cybersecurity practices. This means promoting standardized cybersecurity protocols and fostering communities that can further research in the field.
The CIS is famous for its Critical Security Controls (CSC) guidelines. CIS CSC guidelines include 20 controls that organizations can implement to improve their cybersecurity readiness and response standards.
3 Key Differences and Similarities Between NIST and CIS
NIST and CIS are some of the most well-known organizations when it comes to cybersecurity. They share a common goal of improving cybersecurity standards across the board, which translates to better protection initiatives for sensitive data for both public and private organizations.
1. Neither NIST CSF or CIS CSC Guidelines Are Mandatory
Businesses aren’t forced to follow NIST CSF or CIS CSC guidelines to process sensitive information digitally. Both organizations work on creating comprehensive security standards that any business can adhere to and reference without any limitations.
Improving your organization’s cybersecurity practices can lead to better opportunities. For example, one of the NIST publications, 800-171, outlines necessary guidelines that organizations need to follow if they want to opt for DoD contracts.
Moreover, improving your organization’s cybersecurity is critical if you plan on processing and/or storing client information. Security breaches occur relatively often, and they can impact your business’s reputation due to a lack of proper preparation.
2. CIS CSC Map to Other Cybersecurity Standards
One of the advantages of following the CIS CSC is that its standards directly map to several other compliance guidelines. When comparing CIS controls vs. NIST, the former tend to be much more specific. However, following CIS CSC guidelines means that your organization should also meet NIST CSF standards.
CIS controls are cross-compatible by design to avoid issues with different cybersecurity standards like PCI DSS, GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. CIS and NIST strive for increased cybersecurity across the board, and open standards play a significant role in that goal.
3. Both NIST CSF and CIS CSC Offer Implementation Tiers
If you follow the NIST CSF, then you may be aware that it outlines multiple implementation tiers. Organizations can be categorized under four tiers. On one end of the scale, you have tier-one organizations who exhibit poor cybersecurity practices. Tier-four organizations, on the other hand, reflect the pinnacle of cybersecurity standards.
The CIS CSC uses a different system for categorizing organizations. The latest version of the CSC includes 18 controls that companies should meet. If an organization meets the standards for the first six controls, then it follows basic cybersecurity standards.
Adopting additional controls means that your organization exceeds expectations when it comes to cybersecurity. The more controls you meet, the more prepared your organization will be to face and respond to digital threats.
NIST CSF Mapping to CIS Controls
There’s no one-size-fits-all set of cybersecurity guidelines that every company should follow. Understanding both NIST and CIS standards mean that your organization stands a better chance of being ready to face any cybersecurity threat.
One advantage of CIS CSC over other cybersecurity standards is that it’s cross-compatible by design. If you’re working on meeting NIST CSF standards, you can also adapt your organization to meet CIS controls and vice versa.
Are you not sure what set of cybersecurity standards you should adopt for your organization? Carbide can help you identify and follow the best guidelines for your business. Book a demo today, and let’s get to work on improving your security posture.


