What is the NIST AI RMF 1.0?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly become a cornerstone of innovation across industries—from healthcare and finance to education and manufacturing. Yet, with these advancements come real concerns about bias, privacy, security, and more. The NIST Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Framework (AI RMF 1.0) was developed as a roadmap for organizations looking to harness AI’s benefits while responsibly managing risks.
In this post, we’ll explore the fundamentals of NIST AI RMF 1.0, outline its four core functions, and offer practical guidance on implementing the framework. Whether you’re a startup founder, a data scientist, or an enterprise risk officer, understanding NIST AI RMF 1.0 and its guidelines for safeguarding against potential harms. is essential if you plan to or are using AI in your business operatioms.
NIST AI RMF 1.0 is a comprehensive framework developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with AI systems. This framework:
- Applies to organizations of any size, from startups to large enterprises.
- Is voluntary and flexible, encouraging adoption and adaptation across different sectors.
- Aligns with best practices and can be integrated into existing risk management strategies.
Who Should Use the NIST AI RMF?
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF) is a voluntary, flexible tool that can benefit any organization developing, implementing, or leveraging AI—regardless of size or industry. This includes for-profit businesses, non-profit organizations, and government entities.
While the framework is not mandatory, it provides best practices to help you identify, assess, and mitigate AI risks, ensuring your systems are developed and deployed responsibly.
Importantly, the NIST AI RMF is part of a broader international effort to govern AI in a trustworthy manner. Other standards, such as ISO 42001, also offer controls and guidance for managing security, privacy, and ethical considerations in AI applications.
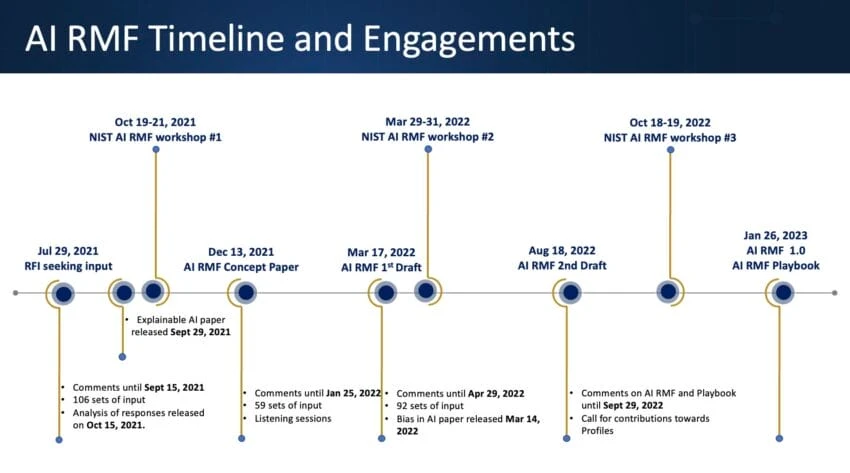
Source: NIST AI RMF Timeline and Engagements
What are the Key Characteristics of the NIST AI RMF?
The NIST AI RMF 1.0 centers on core trustworthiness characteristics of AI systems:
- Valid and Reliable
- Safe
- Secure and Resilient
- Accountable and Transparent
- Explainable and Interpretable
- Privacy enhanced
- Fair with harmful bias managed

Source: AI Risk Management Framework – Resources
Valid and Reliable
Validity ensures that an AI system meets its intended purpose under expected conditions, while reliability ensures it consistently performs without failure over its entire lifecycle. Together, they reduce negative risks, improve trustworthiness, and help confirm that the system’s requirements have been fulfilled.
Safe
Safe AI systems do not endanger human life, health, property, or the environment under defined conditions. This is achieved through responsible design, ongoing monitoring, and contingency planning to prevent or mitigate dangerous outcomes.
Secure and Resilient
Security ensures AI systems maintain confidentiality, integrity, and availability in the face of threats such as adversarial attacks and data poisoning. Resilience means systems can withstand and recover from unexpected adverse events or misuse while continuing essential functions or degrading gracefully.
Accountable and Transparent
Accountability assigns responsibility for AI outcomes and presupposes transparency about system design, data usage, and decision-making processes. Transparency fosters trust by providing appropriate information to stakeholders, enabling oversight, audit, and opportunities for redress when harm occurs.
Explainable and Interpretable
Explainability focuses on clarifying how AI systems generate outputs, while interpretability conveys the meaning and relevance of those outputs to users and stakeholders. Both help people understand and trust AI by shedding light on its decision processes and potential impacts.
Privacy-Enhanced
Privacy in AI aims to protect personal data, identities, and autonomy by minimizing exposure through techniques such as de-identification and privacy-enhancing technologies. These measures help balance confidentiality with other AI goals like accuracy and fairness.
Fair – with Harmful Bias Managed
Fairness involves addressing harmful bias and discrimination so AI does not reinforce existing inequalities or produce unjust outcomes. Organizations manage bias by identifying its sources—systemic, computational, and human-cognitive—and mitigating it throughout the AI lifecycle.
Why the NIST AI RMF 1.0 Matters
With AI increasingly affecting consumer experiences, public policy, and organizational operations, decision-makers need robust methods to ensure trustworthy AI. The NIST AI RMF 1.0:
- Guides you through risk-based decision-making at all stages of an AI system’s lifecycle.
- Helps you align AI initiatives with organizational values and missions.
- Encourages continuous improvement through monitoring and adaptation as AI technology evolves.
The 4 Key Components of the NIST AI RMF
NIST structures the AI RMF 1.0 into four major functions—Govern , Map, Measure, and Manage. Think of these functions as a continuous loop of assessment and improvement.
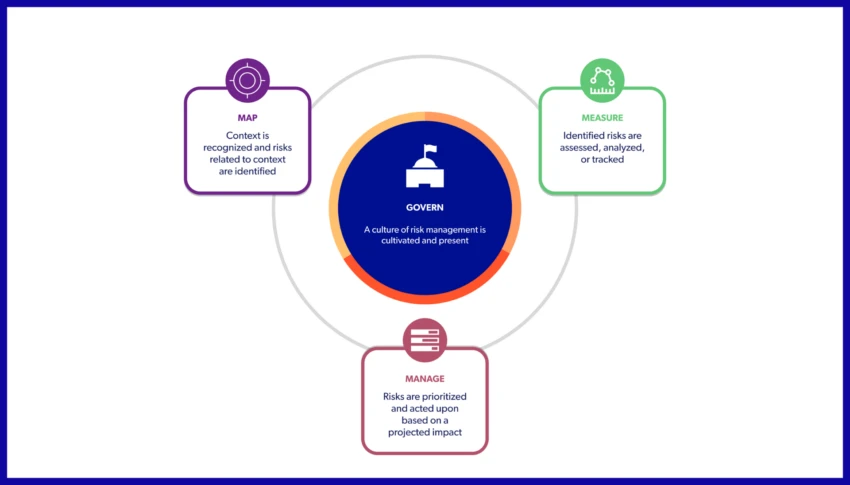
Source: AI Risk Management Framework – Resources
Govern
According to the NIST AI Risk Management Framework, Govern sets the foundation for a risk-aware culture:
- Establish Policies & Processes: Formalize guidelines that ensure accountability for AI outcomes.
- Define Roles & Responsibilities: Identify key stakeholders (developers, compliance teams, executives) and clarify who owns each part of risk management.
- Ensure Accountability: Maintain transparency in decision-making processes, from the initial AI concept to deployment and beyond.
Why It’s Important: Strong governance aligns AI efforts with broader organizational risk tolerance and objectives. It also ensures your team stays on track in managing AI risks proactively rather than reactively.
NIST AI RMF Categories for Govern
(Note: each category contains additional subcategories for more detailed guidance)
Govern 1: Clear, transparent policies, processes, and procedures guide how you map, measure, and manage AI risks.
Govern 2: Accountability structures empower the right individuals and teams, making sure they’re trained and responsible for AI risk handling.
Govern 3: Diversity, equity, inclusion, and accessibility (DEIA) efforts are prioritized when addressing AI risks throughout the lifecycle.
Govern 4: Organizational teams foster a culture dedicated to spotting, discussing, and minimizing potential negative impacts from AI.
Govern 5: Mechanisms exist for robust engagement with relevant AI actors—such as end users, external partners, and impacted communities.
Govern 6: Specific policies tackle risks (and potential benefits) from third-party software, data, and overall supply chain issues.
Map
According to the NIST AI Risk Management Framework, Map is about identifying and contextualizing risks:
- Establish Context: Determine the specific setting in which the AI system will operate, including legal requirements, user needs, and societal expectations.
- Categorize AI Systems: Break down tasks, data sources, and model outputs to clarify function and potential risk areas.
- Map Impacts: Look at how AI could affect individuals and communities—both positively and negatively.
Why It’s Important: Comprehensive mapping reveals where and how an AI system might fail or cause harm, setting the stage for better measurement and management.
NIST AI RMF Categories for Map
(Note: each category contains additional subcategories for more detailed guidance)
Map 1: Establish and document context so everyone understands the environment, legal factors, and stakeholder expectations.
Map 2: Categorize the system’s tasks and methods, identifying its capabilities and limitations for more accurate risk evaluation.
Map 3: Compare AI capabilities, goals, and usage against benchmarks to weigh potential benefits, costs, and organizational fit.
Map 4: Map risks and benefits for all AI system components—including third-party data or tools—to identify vulnerabilities in integrated environments.
Map 5: Characterize impacts to individuals, groups, and society, noting both positive outcomes and potential harms.
Measure
According to the NIST AI Risk Management Framework, Measure involves assessing and benchmarking:
- Select Metrics & Methods: Use both qualitative and quantitative tools to evaluate reliability, accuracy, biases, and other performance indicators.
- Evaluate Trustworthiness: Track how well the AI system meets the trustworthiness characteristics (safety, fairness, etc.).
- Document Findings: Keep a record of results, methodologies, and any corrective actions taken.
Why It’s Important: You can’t manage what you don’t measure. Having a rigorous and repeatable measurement process ensures you detect emergent risks and improvement opportunities.
NIST AI RMF Categories for Measure
(Note: each category contains additional subcategories for more detailed guidance)
Measure 1: Identify and apply the right metrics and methods to thoroughly assess AI risk, including both qualitative and quantitative approaches.
Measure 2: Evaluate AI systems against core trustworthiness criteria—like validity, reliability, safety, privacy, and fairness.
Measure 3: Implement tracking mechanisms that continuously monitor identified risks and capture newly emerging ones over time.
Measure 4: Collect feedback on the effectiveness of current measurements, refining methods and tools to stay accurate and relevant.
Manage
According to the NIST AI Risk Management Framework, Manage is the action phase:
- Prioritize Risks: Rank threats by likelihood and potential impact, focusing on the biggest vulnerabilities first.
- Implement Solutions: Deploy mitigation measures, whether technical fixes (e.g., algorithmic modifications) or organizational policies.
- Continuously Monitor & Improve: Keep iterating, learning from errors, and updating your AI systems to handle new challenges as they arise.
Why It’s Important: An organization that effectively manages risk is better positioned to capitalize on AI while avoiding detrimental outcomes.
AI RMF Categories for Manage
(Note: each category contains additional subcategories for more detailed guidance)
Manage 1: Use insights from Map and Measure to prioritize, respond to, and handle AI risks based on severity and likelihood.
Manage 2: Develop strategies to maximize AI benefits and minimize negative impacts, informed by input from relevant stakeholders.
Manage 3: Manage AI risks and benefits from third-party entities—ensuring consistent oversight and alignment with internal risk policies.
Manage 4: Document your chosen risk treatments (e.g., response, recovery) and maintain communication plans, regularly monitoring for any needed updates.
How to Best Implement the NIST AI RMF?
Coordinate Top-Down Organizational Readiness
- Leadership Buy-In: Executive support is critical for resource allocation and setting a culture of accountability.
- Workforce Training: Ensure AI developers, data scientists, and compliance teams understand AI RMF principles.
- Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion: Form a multidisciplinary, demographically diverse team to spot biases and champion inclusive practices.
Integrating AI RMF 1.0 Into Your Existing Processes
- Enterprise Risk Management (ERM): Align AI risk with cybersecurity, privacy, and operational risk frameworks.
- Documentation & Transparency: Maintain clear records of data sources, training methods, and model changes to enable audits and increase stakeholder trust.
- Third-Party Tools: If you use pretrained models or data sources, assess their risks (e.g., license compliance, malicious data manipulation, or outdated data).
Free Tools and Resources
Future Outlook of AI Risk Management and the NIST AI RMF 1.0
Breakthroughs in generative AI and other large-scale machine learning models present new societal and legal questions, such as intellectual property rights, the potential spread of misinformation, and how to balance privacy with accountability. This, in turn, causes lawmakers and regulatory bodies to pay closer attention to how AI is developed, deployed, and managed.
The NIST AI RMF 1.0 is a “living document” — meaning it will adapt as AI technologies advance and new risks emerge. NIST actively seeks input from diverse stakeholders through public workshops, requests for comment, and collaborative feedback sessions, ensuring the framework addresses real-world challenges and reflects up-to-date best practices. This continuous improvement approach adopted by NIST should also be emulated by organizations and businesses that want to remain proactive and vigilant with their security programs.
Take Your Next Step Toward NIST AI RMF 1.0 Compliance with Carbide
Ready to unlock the full potential of AI while safeguarding your organization and users?
Carbide is here to help. Our robust platform and in-house advisory team do the heavy lifting—embedding best practices for security, privacy, and AI governance right into your organization’s DNA. That means you’ll be able to adapt quickly and efficiently as AI frameworks, like NIST AI RMF 1.0, continue to evolve.
- Assess your current risk management strategy and compare it with NIST AI RMF’s suggestions
- Access the NIST AI RMF resources like the NIST AI RMF Playbook.
- Engage with internal stakeholders and get buy-in from leadership to effectively plan and implement an AI risk management strategy based on the recommendation from the NIST AI RMF 1.0
Book a demo today and discover how we can empower your team to foster responsible, secure, and compliant AI—all under one roof.


