In today’s digital landscape, where data breaches are becoming increasingly sophisticated, securing payment information is not just a compliance requirement – it’s a strategic imperative for businesses around the world. The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), created by the PCI Security Standards Council (PCI SSC), defines the protective measures necessary to guard against evolving threats. With the retirement of PCI DSS v3.2.1 on March 31, 2024, and the advent of PCI DSS v4.0 on April 1, 2024, understanding the purpose and requirements during this transition period is crucial for any business that is involved in payment processing.
What is PCI DSS?
PCI DSS stands for Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. This comprehensive set of guidelines is designed to ensure that all companies involved in processing, storing, or transmitting credit card information maintain a secure environment. Applicable globally, the standard affects a wide range of entities, including merchants of all sizes, payment processors, and service providers, essentially any organization that handles cardholder data (CHD) and sensitive authentication data (SAD).
Why Was PCI DSS Created?
Introduced in 2004, PCI DSS aims to protect credit and debit card transactions against data theft and fraud. As online financial transactions increased, so did the opportunities for cybercriminals, necessitating a unified framework to secure sensitive payment information against bad actors.
What’s Different in PCI DSS v4.0?
The evolution to PCI DSS v4.0 is driven by four primary goals intended to advance payment security standards:
- Evolving Security: Addressing the dynamic security needs of the payment industry to counteract emerging threats.
- Encouraging Continuous Security Practices: Shifting from a compliance checklist to an ongoing security mindset.
- Flexibility in Compliance: Allowing organizations to adopt various methodologies to achieve compliance, acknowledging the diversity in technology and business models.
- Improved Validation and Controls: Introducing more rigorous validation techniques and strengthening security measures.
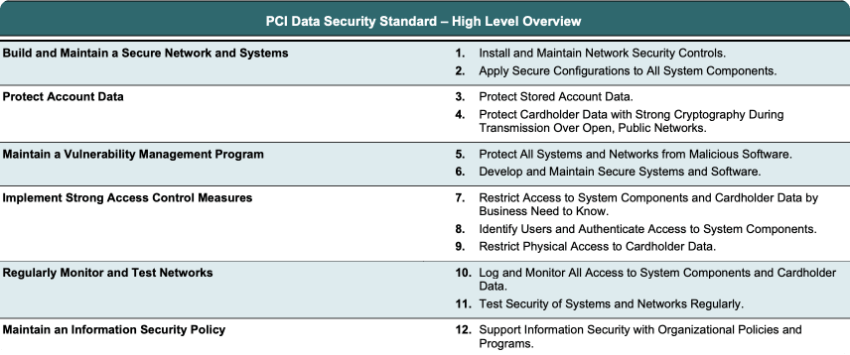
The 12 Principal Requirements for PCI DSS
The core structure of PCI DSS is built around 12 principal requirements, encompassing network security, data protection, vulnerability management, access control measures, monitoring and testing networks, and maintaining an information security policy.
Source: PCI Security Standards Council
Overview of New PCI DSS v4.0 Requirements
The transition to v4.0 introduces several new requirements designed to fortify defenses against current cyber threats. Key changes include:
Enhanced Authentication Protocols: Strengthening authentication mechanisms to protect against unauthorized access.
Increased Flexibility for Customized Implementations: Allowing for more tailored security measures that fit an organization’s specific needs.
Broader Scope for Encryption: Expanding the requirements for encrypting data both at rest and in transit.
Additional PCI DSS requirements for different types of entities include:
- Appendix A1: Additional PCI DSS Requirements for Multi-Tenant Service Providers
- Sections:
- A1.1 Multi-tenant service providers protect and separate all customer environments and data.
- A1.2 Multi-tenant service providers facilitate logging and incident response for all customers.
- Appendix A2: Additional PCI DSS Requirements for Entities Using SSL/Early TLS for Card- Present POS POI Terminal Connections
- Sections:
- A2.1 POI terminals using SSL and/or early TLS are confirmed as not susceptible to known SSL/TLS exploits.
- Appendix A3: Designated Entities Supplemental Validation (DESV)
- Sections:
- A3.1 A PCI DSS compliance program is implemented.
- A3.2 PCI DSS scope is documented and validated.
- A3.3 PCI DSS is incorporated into business-as-usual (BAU) activities.
- A3.4 Logical access to the cardholder data environment is controlled and managed.
- A3.5 Suspicious events are identified and responded to.
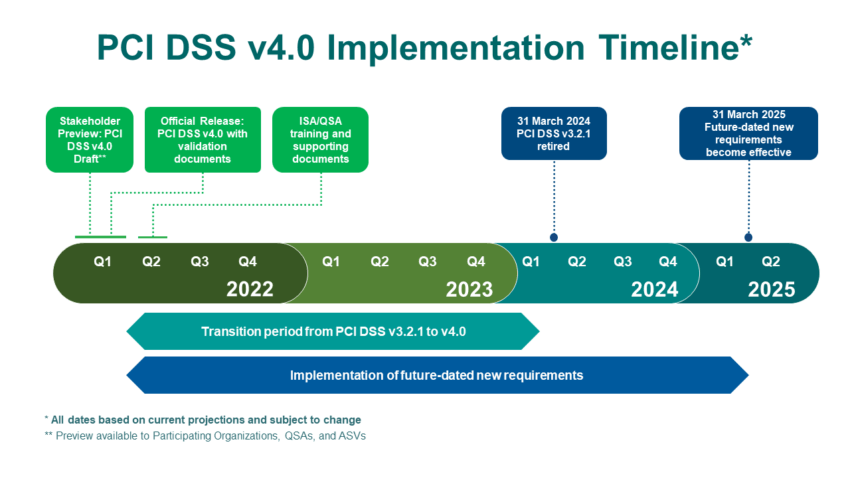
What is the Timeline for PCI DSS v4.0 Implementation?
The three major phases and deadlines to PCI DSS v4.0 implementations are as follows:
- March 31, 2022: Official release of PCI DSS v4.0.
- March 31, 2024: Retirement of version 3.2.1.
- March 31, 2025: Full enforcement of additional v4.0 requirements.
Source: PCI Security Standards Council
Developed with Global Industry Collaboration
PCI DSS v4.0 was developed with the collaboration and feedback from over 200 companies through three rounds of global Request for Comment (RFC) sessions, culminating in a standard that reflects the collective expertise and needs of the industry.
Three Steps to Prepare for PCI DSS v4.0
To navigate the transition effectively:
- Conduct an Internal Audit: Assess your current compliance posture against v4.0 standards.
- Educate Your Team: Ensure that all relevant personnel are aware of the updates and understand their implications.
- Engage with a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA): Leverage their expertise to guide your compliance journey.
The implementation of PCI DSS v4.0 represents a significant step forward in the fight against payment data breaches. By planning and acting now, businesses can ensure they not only meet the updated standard but also enhance their overall security posture.
Don’t wait until the deadline. Reach out to our security experts and start adapting to PCI DSS v4.0 today.